What are HEPA filters?
They are called HEPA filters for their acronym in English (High Efficiency Particulate
Air) whose translation could come to mean something like "high efficiency particulate
air".
HEPA filters need to meet a number of conditions to be considered as such.
In other words, there is a standard that any filter must meet to be considered a HEPA
filter, which means that it must follow specific procedures for its manufacture, pass a
series of tests and have certain labels.
Within the HEPA classification there are subclasses, but there is a level that any
filter must meet in order to have it, and that minimum establishes that it is capable of
capturing at least 99.95% of the particles.
If you do not reach that minimum, you will not be able to trade with such a
rating.
With greater filtration capacity there are the ULPA filters generally used in rooms
where a maximum level of cleanliness in air is required.
There is a big difference between a purifier with a normal filter and one with a much
more advanced
HEPA filter in terms of efficiency
.
Therefore, when an air purification device or any other device that requires a
filtration system comes on the market with a HEPA filter, it can be considered that it
has passed the most exhaustive controls and that it offers the
highest
possible particle retention capacity.
get.
TYPE
FILTER
|
INTEGRAL VALUE
|
LOCAL VALUE
|
|
EFFICIENCY %
|
PENETRATION%
|
EFFICIENCY %
|
PENETRATION%
|
|
H13
|
≥ 99.95
|
≤ 0.05
|
≥ 99.75
|
≤ 0.25
|
|
H14
|
≥ 99,995
|
≤ 0.005
|
≥ 99.975
|
≤ 0.025
|
|
U15
|
≥ 99.9995
|
≤ 0.0005
|
≥ 99.9975
|
≤ 0.0025
|
|
U16
|
≥ 99.99995
|
≤ 0.00005
|
≥ 99.99975
|
≤ 0.00025
|
|
U17
|
≥ 99.999995
|
≤ 0.000005
|
≥ 99.9999
|
≤ 0.0001
|
How do HEPA filters work?
A HEPA filter is a mechanism whose mission is to stop the passage of airborne particles
such as pollen, animal dander, mites, ...
Each type of particle has different dimensions and therefore, a specific measure can be
used to stop some, but not to achieve it with others.
What a HEPA filter does is place different barrier methods
to ensure that the particles that manage to exceed one level are trapped in the
next.
A HEPA filter is made up of a mesh of
randomly placed fibers
.
These fibers are usually layers of cellulose, synthetic fiber and / or glass fibers
arranged in an accordion shape, which means that their surface area is larger and
therefore they have a greater capacity to capture said particles.
The process is carried out gradually:
-
The coarser particles
are trapped by sieving in a first phase, which means that they literally “collide”
with the fibers and cannot continue their advance.
-
Obviously, not all the particles are stopped in this first barrier, but those that
continue their trajectory driven by the air are being trapped in successive
barriers.
Those of medium size
are then intercepted by rubbing with the following fibers, remaining adhered to
them.
-
Finally, those that have managed to circumvent the two previous systems, already
very small in size and imperceptible
to the human being, end up colliding with gas molecules in what is called
diffusion.
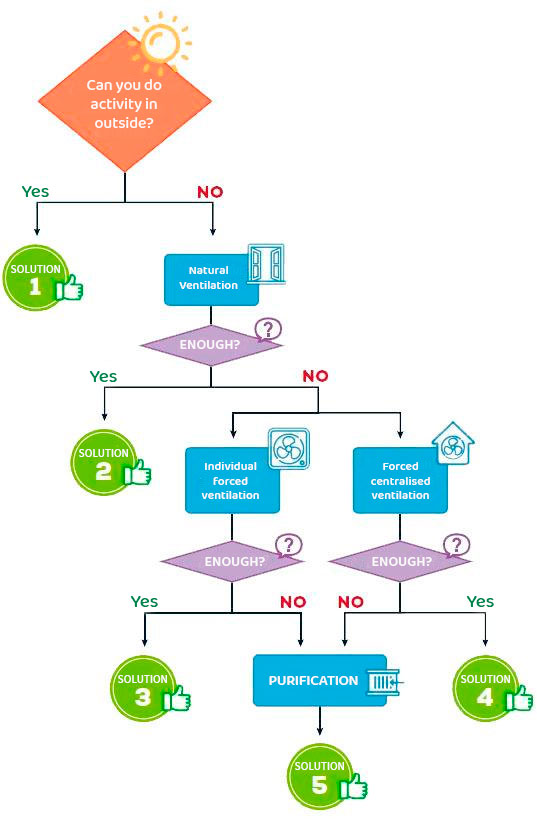
Flow chart for finding solutions
HEPA filters in school classrooms
-
Outdoor activities are always preferable indoors, including breakfast.
-
If the activity is to be indoors, it is preferable in classrooms with the
possibility of natural ventilation, especially cross ventilation (windows
and doors on opposite sides).
-
If natural ventilation is not sufficient, sufficient ventilation can
generally be achieved by using individual exhaust equipment or impellers
with adequate air flow.
-
When centralized forced ventilation systems are available, the outdoor air
rate should be increased and recirculation should be reduced.
-
When all of the above is not possible or is not sufficient, the air must be
purified with equipment equipped with HEPA filters.
-
The final solution can be a combination of options, for example natural
ventilation and purification can be combined.
-
To assess whether a given configuration is sufficient, one of the two
methods described in this guide can be used, both based on CO2 measurements.
-
The use of masks, distance maintenance and hygiene measures are still
necessary in all solutions.
HEPA filter calculator for schools and large venues
The ventilation necessary to reduce the risk of contagion depends on the volume of
the room, the number and age of the occupants, the activity carried out, the
incidence of cases in the region and the risk to be assumed.
The Harvard guide recommends 5-6 air changes per hour for classrooms of 100 m²,
with 25 students aged 5-8 years, and establishes this classification:
Enter the required information and the results will be calculated
automatically.
Current ventilation level
Minimum CADR required
288.41
ft 3 / min
Cubic feet per minute CADR in cfm, for filters that bring only that
unit.
490
m 3 / h
Clean Air Delivery Rate. Filters (individual or multiple, must add this together).